Robotic Automation in Manufacturing Revolutionizing Production Lines

5 min read
Robotic automation is proving to be revolutionary. Robots have completely changed production lines in a variety of industries, increasing productivity, quality, and safety along the way. This blog post examines the revolutionary effects of robotic automation in manufacturing, covering its advantages, uses, difficulties, and potential future developments.
The term “robotic automation” describes the use of automated systems and robots to perform a variety of jobs in manufacturing operations. The purpose of these robotic systems is to perform repetitive tasks accurately, quickly, and diligently without the need for human intervention. It has evolved with technological improvements, allowing manufacturers to increase productivity and spur growth.
Benefits of Robotic Automation in Manufacturing
The following are the some of the benefits of automation in manufacturing:
-
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
A primary benefit of robotic process automation in the manufacturing sector is the notable increase in productivity and efficiency. Robots are able to operate continuously, reducing downtime and increasing productivity. Higher production rates and shorter cycle durations result from their ability to complete jobs at a steady pace without human error or exhaustion.
-
Improved Quality and Accuracy
Robots are designed to carry out jobs with accuracy and precision, ensuring consistently high-quality output. It reduces errors and rejects them by doing away with human error and deviation, which raises the quality of the final output. This degree of accuracy is especially helpful in sectors where accuracy is essential, such as the automobile, electronics, and pharmaceutical industries.
-
Enhanced Workplace Safety
By eliminating the need for people to undertake dangerous or physically taxing jobs, it has greatly increased workplace safety. Without endangering human health or safety, robots are able to carry big weights, operate in hot or poisonous settings, and carry out repeated tasks. It reduces workplace accidents and enhances workers’ general well-being.
-
Cost Savings
Even though robotic process automation may require a large initial investment, there will be significant long-term cost benefits. In comparison to human labour, robots can work continuously without overtime compensation or breaks and require less maintenance. Through the optimization of resource usage and labour cost reduction, firms can realize significant cost reductions in the long run.
-
Flexibility and Adaptability
Manufacturers can quickly adjust to shifting market demands through smart automation. It is simple to program or modify robots to perform a variety of tasks or switch across product lines. This makes it possible for manufacturers to grow their businesses effectively and react quickly to changes in the market.
Read more: AI And Robotics Advancements in Automation
Applications of Robotic Automation in Manufacturing
Robotics applications in manufacturing have revolutionized production processes, enhancing efficiency and precision through the deployment of automated systems that handle tasks ranging from assembly and welding to packaging, contributing to increased productivity and product quality.
-
Assembly and Disassembly
Robots are particularly good at high-precision repetitive assembly jobs like soldering, screw tightening, and component placement. They are able to ensure constant quality throughout the assembly process and handle sensitive parts with care. In a similar vein, robots are adept at gently removing parts of things without endangering them.
-
Material Handling and Transport
Material handling and transportation within production facilities have been transformed by robotic process automation. Robots that have sensors and vision systems can identify, pick, put, and move materials with efficiency. They can securely handle challenging areas, maximizing the use of warehouse space and lowering the possibility of human error.
-
Quality Inspection
A vital component of production procedures is quality inspection, which ensures both product compliance and customer pleasure. Robots with smart sensors and cameras can measure objects precisely, identify abnormalities, and check them for defects. It lowers the need for human inspection and related expenses while simultaneously enhancing quality control.
-
Packaging and Palletizing
Due to the automation of these labor-intensive jobs, robots have completely changed the packing and palletizing industry. Their abilities include
- Managing various packing styles
- Properly applying labels or wrapping materials
- Organizing goods on pallets with efficiency.
Packaging robots not only speed up the process but also minimize mistakes and use materials more efficiently.
-
Welding and Joining
In industrial sectors where accurate and reliable welds are essential, robotic welding has become the norm. When given welding tools, robots can execute intricate welding tasks with remarkable precision and consistency. Their adaptability in handling various materials and welding techniques results in better weld quality and less rework.
Difficulties Associated with Robotic Automation in Manufacturing
Although it has several advantages, producers must overcome certain obstacles in order to apply it:
-
High Initial Investment
The upfront costs associated with obtaining smart automation systems can be high and include the cost of the robots themselves, programming, integration with the current infrastructure, and employee training. This upfront cost could discourage some manufacturers from implementing automation.
-
Technical Complexity
Robotics integration, programming, and maintenance technical know-how are prerequisites for implementing automation. To properly manage robot systems, manufacturers might need to recruit expert professionals or invest in training their workers.
-
Limited Task Variety
Robots may find it difficult to perform intricate or unusual activities that call for human creativity or decision-making abilities, even though they are excellent at repeated chores. Manufacturers must carefully evaluate the jobs that are most suitable for smart automation.
-
Workforce Adaptation
Concerns about job security or a fear of being replaced by robots may arise among the current workers when robots are introduced into the manufacturing environment. Manufacturers need to address these issues with open communication, opportunities for retraining, or redeployment into more valuable roles.
-
Maintenance and Downtime
Robots still require routine servicing and repairs, even if they require less upkeep than humans. Random system breakdowns or downtime may have an influence on production deadlines. To reduce downtime and increase production, manufacturers need to have a strong maintenance strategy in place.
What Prospects Does Robotic Automation in Manufacturing Have Going Forward?
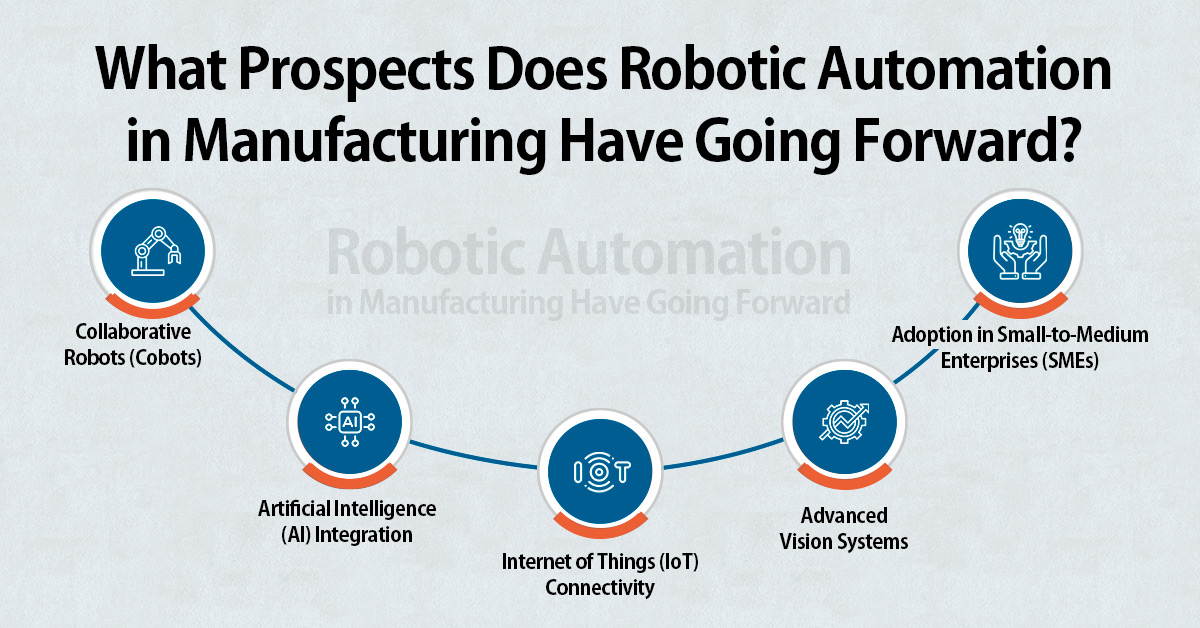
As technology develops, industrial automation and robotics appears to have a bright future.
-
Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Often referred to as cobots, collaborative robots are made to operate alongside people, supporting them in activities that call for human dexterity or decisions. Cobots, which enable human-robot collaboration on the manufacturing line, can aid in bridging the gap between manual work and full automation.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
Intelligent decision-making, adaptive learning, and autonomous operation are made possible by the combination of robotic process automation with artificial intelligence. Robots with AI capabilities can anticipate maintenance requirements, optimize production procedures, evaluate data in real-time, and even self-program in response to changing circumstances.
-
Internet of Things (IoT) Connectivity
When manufacturing equipment and robots are connected via the Internet of Things, real-time monitoring and easy data sharing are made possible. Manufacturers are able to obtain important information on production patterns, machine performance, and the need for predictive maintenance through this connectivity, which promotes continuous improvement.
-
Advanced Vision Systems
Robots can now see their environment more reliably and accurately by developments in vision systems. Robots can now detect faults, scan labels or barcodes, recognize things, and even detect small variations in product quality by the combination of machine learning algorithms and high-resolution cameras.
-
Adoption in Small-to-Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
Small-to-medium-sized businesses (SMEs) are anticipated to adopt smart automation as it becomes more widely available and reasonably priced. These companies may grow their operations, increase production, and become more competitive by utilizing AI technology without having to pay large upfront expenses.
Conclusion
Robotic automation has altered manufacturing production lines by providing greater flexibility, cost savings, safety, quality, and efficiency. Robots are used for everything from welding and quality control to assembly and material handling. With the advent of collaborative robots, AI integration, IoT connectivity, enhanced vision systems, and increased use among SMEs, robotic process automation appears to have bright prospects despite implementation obstacles. Manufacturers who want to remain competitive in the rapidly changing industrial landscape of today must embrace robotic automation.
Published: December 29th, 2023